What Are Your Father’s Rights In Texas?
Are you the father of a child in Texas and Mom is refusing to let you see or communicate with your child? Are you paying child support in Texas for your child, yet Mom tries to dominate all interaction between you and the child to suit her needs. Is this Parental Alienation in the present or a step commencing down that path?
Fathers have rights in Texas and because this is one of the more frequent calls we receive from Dads, I thought it was time to discuss some specific law from the Texas Family Code regarding the rights and duties afforded to a Parent, whether Mom or Dad!
Under the Texas Family Code a “Parent” is defined as the mother, a man presumed to be the father, a man legally determined to be the father, a man who has been adjudicated to be the father by a court of competent jurisdiction, a man who acknowledged his paternity under applicable law or an adoptive mother or father.
Tex. Fam. Code Sec. 160, otherwise known as the Uniform Parentage Act, states that a man is presumed to be the father of a child if:
1. he is married to the mother of the child and the child is born during the marriage;
2. he is married to the mother of the child and the child is born before the 301st day after the date the marriage is terminated by death, annulment, declaration of invalidity, or divorce;
3. he married the mother of the child before the birth of the child in apparent compliance with law, even if the attempted marriage is or could be declared invalid, and the child is born during the invalid marriage or before the 301st day after the date the marriage is terminated by death, annulment, declaration of invalidity, or divorce;
4. he married the mother of the child after the birth of the child in apparent compliance with law, regardless of whether the marriage is or could be declared invalid, he voluntarily asserted his paternity of the child, and:
a)the assertion is in a record filed with the bureau of vital statistics;
b) he is voluntarily named as the child’s father; or
c) he promised in a record to support the child as his own; or
5. during the first two years of the child’s life, he continuously resided in the household in which the child resided and he represented to others that the child was his own.
If the above applies to you and you have established legal standing to support that you are “the father,” what are your rights and duties as the Texas Family Code Sec. 151.001 states:
§ 151.001. Rights and Duties of Parent
(a) A parent of a child has the following rights and duties:
(1) the right to have physical possession, to direct the moral and religious training, and to designate the residence of the child;
(2) the duty of care, control, protection, and reasonable discipline of the child;
(3) the duty to support the child, including providing the child with clothing, food, shelter, medical and dental care, and education;
(4) the duty, except when a guardian of the child’s estate has been appointed, to manage the estate of the child, including the right as an agent of the child to act in relation to the child’s estate if the child’s action is required by a state, the United States, or a foreign government;
(5) except as provided by Section 264.0111, the right to the services and earnings of the child;
(6) the right to consent to the child’s marriage, enlistment in the armed forces of the United States, medical and dental care, and psychiatric, psychological, and surgical treatment;
(7) the right to represent the child in legal action and to make other decisions of substantial legal significance concerning the child;
(8) the right to receive and give receipt for payments for the support of the child and to hold or disburse funds for the benefit of the child;
(9) the right to inherit from and through the child;
(10) the right to make decisions concerning the child’s education; and
(11) any other right or duty existing between a parent and child by virtue of law.
Both parents have these rights unless a court order has created, modified, ordered, or delegated the statuary rights of a parent. The rights you have will support and empower you in a hands on relationship with your child.
All parents have the right to have a relationship with their children! One misguided parent may attempt to employ parental alienation to hurt the other parent and cause the child to be denied a loving relationship with the other parent. Know your rights and contact an attorney who can help you and your child fulfill a meaningful relationship!
Child Abuse and Family Violence in Texas
The Texas Family Code defines Family Violence as an act by a member of the family or household against another member that is intended to result in physical harm, bodily injury, assault, or a threat on a family member in danger of imminent physical harm. This abuse is defined as physical injury that results in substantial harm or genuine threat of sexual, intercourse or conduct; or encouraging the child to engage in sexual conduct.
What does “family” include? Individuals related by blood or affinity, marriage or former marriage, biological parents of the same child, foster children, and members or former members of the same household (including roommates).
What about child abuse?
Some very interesting statistics:
-
A report of child abuse is made every ten seconds
-
More than four children die every day as a result of child abuse
-
70% of children that die from abuse are under age of 4
-
Child abuse occurs at every socioeconomic level within all ethnic and cultural lines and all religions and all levels of education!
-
Approximately 30% of abused and neglected children will later abuse their own children
Statistics re: childhelp.org
In Texas (2008 Crime in Texas.com), victims are primarily female (75%) and the offenders are primarily male (77%). The primarily weapon involved in family violence is physical force with the use of hands, feet or fists (78%).
How can you know if child abuse exists in a household?
Look for these most common child abuse indicators in children:
-
Injuries that are unexplained
-
Major and sudden changes in a child’s behavior
-
Return to earlier behavior: such as bed wetting, thumb sucking, and fear of dark or strangers or more serious language or memory problems
-
Serious fear of going home
-
Changes in eating or sleeping habits
-
Changes in school performance or attendance
-
Lack of personal care or hygiene
-
New risk taking behaviors
-
Inappropriate sexual behavior
If you are a family member, friend, teacher, or child-care giver of a child who has started displaying very different behaviors or showing injuries, it is imperative that you contact someone who can either help this child or prevent any more family violence from occurring in this child’s family. This child and family need help now!
 
Texas Child Support Guidelines Update
PLEASE READ UPDATE (2019)
Texas Child Support Guidelines Change-
Effective Sept. 1, 2019
Effective September 1, 2019 The Texas Child Support Division of the Attorney General increased the Maximum child Support under the Texas Child Support Guidelines from $8,550 to the “new cap”of net monthly resources to $9200 annually. This change in the law will increase the amount of maximum child support from of $1,710.00 to $1,840.00 monthly (20% of $9200. For one child)
CLICK TO READ MORE ON THIS UPDATE
PRIOR GUIDELINES
On September 1, 2013: Important Texas Child Support Guideline Changed!
The Texas Child Support Division of the Attorney General increased the “CAP” on net resources for purposed Child Support from the past amount of $7500 to be $8550, which became effective Sept. 1, 2013.
This “Cap Increase” affects any child support case filed or pending after September 1, 2013.
Under the Texas Family Code §154.125 the guidelines for Child Support are as follows:
(a) The guidelines for the support of a child in this section are specifically designed to apply to situations in which the obligor’s monthly net resources are not greater than $8,500 or the adjusted amount determined under Subsection (a-1), whichever is greater.
(a-1) The dollar amount prescribed by Subsection (a) above is adjusted every six years as necessary to reflect inflation. The Title IV-D agency shall compute the adjusted amount, to take effect beginning September 1 of the year of the adjustment, based on the percentage change in the consumer price index during the 72-month period preceding March 1 of the year of the adjustment, as rounded to the nearest $50 increment. The Title IV-D agency shall publish the adjusted amount in the Texas Register before September 1 of the year in which the adjustment takes effect. For purposes of this subsection, “consumer price index” has the meaning assigned by Section 341.201, Finance Code.
(a-2) The initial adjustment required by Subsection (a-1) shall take effect September 1, 2013. This subsection expires September 1, 2014.
(b) if the obligor’s monthly net resources are not greater than the amount provided by Subsection (a), the court shall presumptively apply the following schedule in rendering the child support order:
CHILD SUPPORT GUIDELINES
BASED ON THE MONTHLY NET RESOURCES OF THE OBLIGOR
- 1 child 20% of Obligor’s Net Resources
- 2 children 25% of Obligor’s Net Resources
- 3 children 30% of Obligor’s Net Resources
- 4 children 35% of Obligor’s Net Resources
- 5 children 40% of Obligor’s Net Resources
- 6+ children Not less than the amount for 5 children
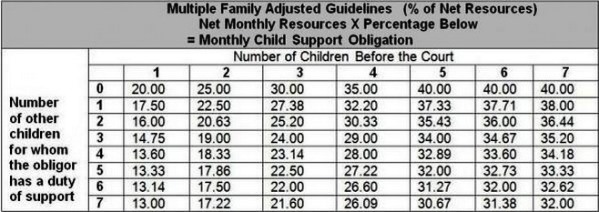
Depending on the number of other children an obligor has a duty to support, the percentage of child support may be lower. For example, if the obligor was previously married and has 1 child to support in the previous marriage, the amount of support paid for one child before the court decreases to 17.50 percent. See the chart below.
Net resources are determined by deducting the following from the obligor’s income:
1. Social Security Taxes;
2. Federal Income Tax based on the tax rate for a single person claiming one personal exemption and the standard deductions;
3. State Income Tax;
4. Union Dues (if such deductions are being withheld); and
5. Expenses for Health Insurance Coverage for Obligor’s Child(ren) (if such deductions are being withheld).
Divorce: What is separate property and what is community property?
Under the Texas Family Code, a spouses separate property consists of 1) the property owned or claimed by the spouse before marriage; 2) the property acquired by the spouse during marriage by gift, devise, or descent, and 3) the recovery for personal injuries sustained by the spouse during marriage, except any recovery for loss of earning capacity during marriage.
The terms “owned and claimed” as used in the Texas Family Code mean that where the right to the property accrued before marriage, the property would be separate. Inception of title occurs when a party first has a right of claim to the property by virtue of which title is finally vested. The existence or nonexistence of the marriage at the time of incipiency of the right of which title finally vests determines whether property is community or separate. Inception of title occurs when a party first has a right of claim to the property.
Under Texas Constitution, Art. XVI, Section 15, separate property is defined as all property, both real and personal, of a spouse owned or claimed before marriage, and that acquired afterward by gift, devise or descent, shall be the separate property of that spouse; and laws shall be passed more clearly defining the rights of the spouses, in relation to separate and community property; provided that persons about to marry and spouses, without the intention to defraud pre-existing creditors, may by written instrument from time to time partition between themselves all or part of their property, then existing or to be acquired, or exchange between themselves the community interest of one spouse or future spouse in any property for the community interest of the other spouse or future spouse in other community property then existing or to be acquired, whereupon the portion or interest set aside to each spouse shall be and constitute a part of the separate property and estate of such spouse or future spouse; spouses may also from time to time, by written instrument, agree between themselves that the income or property from all or part of the separate property then owned or which thereafter might be acquired by only one of them, shall be the separate property of that spouse; if one spouse makes a gift of property to the other that gift is presumed to include all income or property which might arise from that gift of property; and spouses may agree in writing that all or part of the separate property owned by either or both of them shall be the spouses’ community property.
In 1917 the Legislature defined and income from separate property to be the separate property of the owner spouse. In Arnold v. Leonard, 114 Tex. 535,273 S.W. 799 (1925), the Supreme Court held that the Legislature did not have the constitutional authority to characterize the income from separate property as the owner’s separate property. The court explained that the Legislature’s authority was limited to enacting laws regulating the management and liability of marital property, not its separate or community character. This decision strengthened the constitutional principal that the Legislature may not define what is community and separate property in a manner inconsistent with Article 16, Section 15 of the Texas Constitution.
There are numerous means by which separate property may be acquired in defiance of Article 16, Section 15, a partial list includes mutations of separate property, increases in value of separate land and personality, recovery for personal injury not measured by loss of earning power, improvements of separate land with an unascertainable amount of community funds, and United States Securities purchased with community funds.
Although such property may undergo changes or mutations, as long as it is traced and properly identified it will remain separate property.
The Texas Family Code defines community property as follows: “community property consists of the property, other than separate property, acquired by either spouse during marriage.”
Texas Family Code, Section 3.003 states that all property possessed by either spouse during or at the dissolution of the marriage is presumed to be community property and that the degree of proof necessary to establish that property is separate property, rather than community property, is clear and convincing evidence. Clear and convincing evidence is defined as that measure or degree of proof that will produce in the mind of the trier of fact a firm belief or conviction as to the truth of the allegations sought to be established. If property cannot be proved to be separate property, then it is deemed to be community property.
The Texas Family Code, Section 7.002, deals with quasi-community property and requires a court divide property wherever the property is situated, if 1) the property was acquired by either spouse while domiciled in another state and the property would have been community property if the spouse who acquired the property had been domiciled in Texas at the time of acquisition; or 2) property was acquired by either spouse in exchange for real or personal property and that property would have been community property if the spouse who acquired the property so exchanged had been domiciled in Texas at the time of the acquisition.