Need to Know About Spousal Maintenance Laws in Texas?
Texas spousal maintenance can be a useful and effective tool in a divorce. A spouse lacking sufficient property or the means to provide for his/her minimum reasonable needs, may have awarded additional funds from the other spouse during the divorce and after to help rebuild his/her life following their divorce.
In September of 2011, the Texas Legislature revised and modified the requirements for spousal maintenance including the limits on amounts and duration of time allowed.
The eligibility requirements of the Texas spousal maintenance law is still considered one of the more restrictive spousal maintenance laws in the U.S.
To be able to be awarded Spousal Maintenance (statutory term for spousal support or alimony) you must be married and the spouse seeking support must lack sufficient property to provide for the spouse’s “minimum reasonable needs”. Also one of the following is required:
-
The recipient must be unable to earn sufficient income to provide for his or her minimum reasonable needs because of an incapacitating mental or physical disability.
-
The marriage lasted for 10 years or longer and the recipient lacks the ability to earn sufficient income to provide for his or her minimum reasonable needs.
-
The recipient is the custodian of a child of the marriage of any age who requires substantial care and personal supervision because of a physical or mental disability that prevents the spouse from earning sufficient income to provide for the spouse’s minimum reasonable needs.
-
The person ordered to pay support was convicted of or received deferred jurisdiction for an act of family violence during the pendency of the suit or within two years of the date the suit was filed.
The Maximum Amount of spousal maintenance the courts may award is $5,000 per month, although it is still limited to 20 percent of the Payer’s average Gross Monthly Income.
The Maximum Duration of Time for spousal maintenance is:
-
Five years if the marriage is 10 years or less and the eligibility for spousal maintenance is established by an act that constitutes family violence.
-
Five years if the length of marriage is at least 10 years but no more than 20 years.
-
Seven years if the marriage length was at least 20 years but no more than 30 years.
-
Ten years if the marriage length lasted 30 years or longer.
In cases where the spousal maintenance is awarded due to the mental or physical disability of the spouse or a child of the marriage, the court may order the maintenance continue as long as the disability continues.
The spousal maintenance awarded by the court is discretionary and may not always eliminate the shortfall of the requesting spouse’s monthly expenses.
What about Termination of Spousal Maintenance? The obligation to pay future maintenance terminates on the death of either party or on the remarriage of the spouse receiving the maintenance.
If the court finds that the receiving spouse cohabits with another person and is in a dating or romantic relationship in a permanent place of abode on a continuing basis, the court shall order the termination of the maintenance obligation.
Termination of the maintenance obligation does not terminate the obligation to pay any maintenance that accrued before the date of termination and this amount will have to be paid or a judgment will be enforced by the court.
If you are thinking about a divorce in Texas and have questions concerning your eligibility for spousal maintenance contact a legal professional to help you through this process.
Temporary Spousal Maintenance in Texas
In any Divorce case a father or husband should expect two attacks right out of the door. First, is paying for child support because most District Judges in Dallas, Tarrant, and Collin counties do not look favourably on 50/50 custody during temporary orders. Second, is paying temporary spousal maintenance to the wife.
Temporary spousal maintenance is essentially money that the Court forces a husband to pay his wife during the pendency of the divorce. Unfortunately, the District Judge has broad discretion in awarding the amount and duration of the temporary spousal maintenance. The temporary spousal maintenance is awarded based on considerations of both the degree to which the Spouse is destitute of means to pay for her necessities during the pendency of the suit and the ability of the Husband to pay.
Essentially, these considerations are determined by the Judge and if the Spouse has no job or means to support herself then, the Husband should expect a large percentage of his paycheck to go to the Spouse for the duration of the case. In many cases, if the Ex-Wife has the means to support herself, the Court will still award her spousal maintenance to some extent. The amount that the Court fixes as temporary spousal maintenance is likely permanent until the conclusion of the case and only appealable on mandamus. Usually, the appeal will cost more than paying the Spouse. Unfortunately, the Court uses temporary spousal maintenance to help settle cases by forcing the Husband to support both individuals of the party.
If you are seeking a divorce and have a job that provides well for your family, prepare to be attacked for child support and temporary spousal maintenance for the duration of the case. To mitigate the temporary spousal maintenance amount and seek 50/50 custody with your children, find an experienced attorney that can prepare you for the temporary orders. Temporary spousal maintenance is a tool the Court uses to equalize the estate and force a compromise. Divorce is a painful process and temporary spousal maintenance makes the process even more painful, but regrettably the burden primarily falls upon the Husband’s neck.
Julian Nacol
Nacol Law Firm PC
Spousal Maintenance Law for a Texas Divorce
The origin and basis of family law statutes and precedent in Texas were heavily influenced by the predecessor Spanish/Mexican Law prior to the formation of the Texas Republic. Spanish Law required in large measure that a husband and wife share ownership and if a divorce was granted then a 50/50 split of all property would ensue. Though there are exceptions to this, a general tenant of Texas property law states that both spouses will receive half of all the property they accrue during the marriage called “community property”, not inherited or received by gift. The influence of Spanish Law is a primary reason that for many years Texas has not favored any type of permanent alimony (also called spousal maintenance) after divorce.
In 1995 the Texas Legislature passed the first Spousal Maintenance Law that allowed a limited type of alimony. The law has been amended many times but in its current form it allows, upon proper proof, a spouse, under specific conditions to receive post-divorce money from their spouse for future support. The eligibility for Spousal Maintenance in Texas is limited and narrowly constructed.
Texas Family Code 8.051 states the requirements for a spouse to be eligible for Spousal Maintenance (alimony) as follows:
The spouse in which requests the spousal maintenance has been a victim of family violence by their husband or wife and the offense occurred:
- within two years before the date on which a suit for dissolution of the marriage is filed or;
- while the suit is pending
OR
The spouse seeking spousal maintenance:
- is unable to earn sufficient income to provide for the spouse’s minimum reasonable needs because of an incapacitating physical or mental disability;
- has been married to the other spouse for 10 years or longer or lacks the ability to earn sufficient income to provide for the spouse’s minimum reasonable needs; or
- is the custodian of a child of the marriage of any age who requires substantial care and personal supervision because of a physical or mental disability that prevents the spouse from earning sufficient income to provide for the spouse’s minimum reasonable needs.
The qualifications are narrow. Spousal Maintenance focuses on a spouse who has been a victim of family violence, has a mental or physical disability, or has been married for at least 10 years. The amount of money the Court will allow to be paid to a spouse monthly cannot exceed the lessor of 5,000 or 20% of a spouse’s average monthly gross income per Texas Family Code 8.005.
If you are in the process of divorce, and have been a victim of family violence or have been married for at least 10 years, then speak with an experienced attorney about the possibility of obtaining Spousal Maintenance. Spousal Maintenance is not a permanent fix but a temporary solution until you can get back on your feet. Texas Courts are hesitant in granting spousal maintenance because the spouse of a marriage generally receives half of all property accrued during the marriage. If the required extraordinary circumstances are present it is possible to receive some type of alimony for a limited amount of time.
Contact an experienced attorney that deals with matters to inform you if spousal maintenance is possibility. If you have been a victim of family violence or have been a stay at home mom for at least 10 years then you may have the ability to receive a limited form of alimony to help aid you with the daunting task of finding a new job and starting a new life.
What About Texas Spousal Support Laws ?
In September 1, 2011, Texas House Bill 901 ( Texas HB 901 ) revised the spousal maintenance law in the Texas Family Code effective for divorce cases filed on or after September 1, 2011. The bill revised the conditions that establish eligibility for spousal maintenance, commonly referred to as alimony, and changes the factors required to be considered by a court in determining the nature, amount, duration, and manner of periodic payments for a spouse who is eligible to receive maintenance.
Eligibility for spousal maintenance still requires that the spouse seeking maintenance lacks sufficient property to provide for the spouse’s minimum reasonable needs.
The law provides potentially increased relief to spouses who have been out of the work force, are disabled, are victims of family violence or are the primary custodians of a disabled child.
Some of the major items in the Texas Spousal Support Law are:
1. The maximum amount of spousal support that courts may award increased from $2,500 to $5,000.00 per month, although it is still limited to 20 percent of the payer’s average gross monthly income.
2. The duration of spousal support in Texas is a maximum of 5, 7 or 10 years, generally depending on the length of the marriage.
3. The law clarifies if a person has primary care for a disabled child, the custodial parent may be prevented because of the child’s disability from earning sufficient income to meet the custodial parent’s minimum reasonable needs.
4. The law also clarifies a person may not be held in contempt for failing to pay spousal support which is in an agreed order and extends beyond the period of time provided under the law.
In order to receive “maintenance,” (which is the statutory term for spousal support), the spouse seeking support must lack sufficient property to provide for the spouse’s “minimum reasonable needs”, AND one of the following:
(1) The recipient must be unable to earn sufficient income to provide for his or her minimum reasonable needs because of an incapacitating mental or physical disability;
(2) The marriage lasted for 10 years or longer and the recipient lacks the ability to earn sufficient income to provide for his or her minimum reasonable needs;
(3) The recipient is the custodian of a child of the marriage of any age who requires substantial care and personal supervision because of a physical or mental disability that prevents the spouse from earning sufficient income to provide for the spouse’s minimum reasonable needs; OR
(4) The person ordered to pay support was convicted of or received deferred jurisdiction for an act of family violence during the pendency of the suit or within two years of the date the suit is filed.
The court can order maintenance to continue for:
(1) 5 years if the parties were married less than 10 years and the maintenance is awarded due to family violence;
(2) 5 years if the parties were married more than 10 years, but less than 20 years.
(3) 7 years if the parties were married more than 20 years, but less than 30 years;
(4) 10 years if the parties were married for more than 30 years.
In cases where the maintenance is awarded due to the mental or physical disability of the spouse or a child of the marriage, the court may order that the maintenance continue as long as the disability continues.
However, in all circumstances, the law provides that the Court shall order maintenance for the shortest reasonable period that allows the recipient to earn sufficient income to meet his or her reasonable needs.
What about Termination?
a. The obligation to pay future maintenance terminates on the death of either party or on the remarriage of the oblige.
b. After a hearing, the court shall order the termination of the maintenance obligation if the court finds that the obligee cohabits with another person with whom the obligee has a dating or romantic relationship in a permanent place of abode on a continuing basis.
c. Termination of the maintenance obligation does not terminate the obligation to pay any maintenance that accrued before the date of termination, whether as a result of death or remarriage
If you are contemplating dissolving your marriage and have questions concerning your financial future, seek competent legal counsel to help you determine whether you could be eligible for spousal support the provisions of the law.
Texas Divorce Spousal Maintenance Calculator
Texas is one of the most restrictive states when it comes to ordering spousal support; or “maintenance” as it is defined in the Texas statute. Texas House Bill 901 changing the spousal maintenance law in the Texas Family Code became effective for divorce cases on September 1, 2011. The bill revised the conditions that establish eligibility for spousal maintenance, commonly referred to as alimony and changed the factors required to be considered by a court in determining the nature, amount, duration, and manner of periodic payments for a spouse who is eligible to receive maintenance.
The court that determines a spouse is eligible to receive maintenance shall determine the nature, amount, duration, and manner of periodic payments by considering all relevant factors, including:
(1) each spouse’s ability to provide for that spouse’s minimum reasonable needs independently, considering that spouse’s financial resources on dissolution of the marriage;
(2) the education and employment skills of the spouses, the time necessary to acquire sufficient education or training to enable the spouse seeking maintenance to earn sufficient income, and the availability and feasibility of that education or training;
(3) the duration of the marriage;
(4) the age, employment history, earning ability, and physical and emotional condition of the spouse seeking maintenance;
(5) the effect on each spouse’s ability to provide for that spouse’s minimum reasonable needs while providing periodic child support payments or maintenance, if applicable;
(6) acts by either spouse resulting in excessive or abnormal expenditures or destruction, concealment, or fraudulent disposition of community property, joint tenancy, or other property held in common;
(7) the contribution by one spouse to the education, training, or increased earning power of the other spouse;
(8) the property brought to the marriage by either spouse;
(9) the contribution of a spouse as homemaker;
(10) Marital misconduct, including adultery and cruel treatment, by either spouse during the marriage; and
(11) Any history or pattern of family violence, as defined by Section 71.004 of the Texas Family Code.
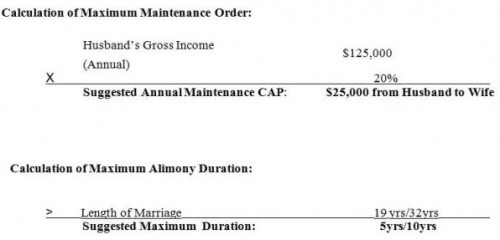
The maximum amount of spousal support that courts may award is the lesser of $5,000.00 per month or 20 percent of the payer’s average gross monthly income. This is the maximum amount of maintenance the court orders.
However, in all circumstances, the law provides that the Court shall order maintenance for the shortest reasonable period that allows the recipient to earn sufficient income to meet his or her “minimum reasonable needs” and as follows:
The Texas law mandates the maximum duration of support as follows:
Maintenance shall be paid for a maximum of:
• 5 years, if due to family violence conviction and marriage is under 10 years;
• 5 years, if marriage is between 10 and 20 years;
• 7 years, if marriage is between 20 and 30 years;
• 10 years, if marriage is 30 years or more;
except in the case of an incapacitating physical or mental disability, in which case the award may last as long as the disability.
In addition, the law allows the Texas Family Law Courts to terminate maintenance if the recipient “cohabits with another person in a permanent place of abode on a continuing, conjugal basis.”
Sample Calculation of Texas Spousal Support Maintenance: