Texas Divorce Spousal Maintenance Calculator
Texas is one of the most restrictive states when it comes to ordering spousal support; or “maintenance” as it is defined in the Texas statute. Texas House Bill 901 changing the spousal maintenance law in the Texas Family Code became effective for divorce cases on September 1, 2011. The bill revised the conditions that establish eligibility for spousal maintenance, commonly referred to as alimony and changed the factors required to be considered by a court in determining the nature, amount, duration, and manner of periodic payments for a spouse who is eligible to receive maintenance.
The court that determines a spouse is eligible to receive maintenance shall determine the nature, amount, duration, and manner of periodic payments by considering all relevant factors, including:
(1) each spouse’s ability to provide for that spouse’s minimum reasonable needs independently, considering that spouse’s financial resources on dissolution of the marriage;
(2) the education and employment skills of the spouses, the time necessary to acquire sufficient education or training to enable the spouse seeking maintenance to earn sufficient income, and the availability and feasibility of that education or training;
(3) the duration of the marriage;
(4) the age, employment history, earning ability, and physical and emotional condition of the spouse seeking maintenance;
(5) the effect on each spouse’s ability to provide for that spouse’s minimum reasonable needs while providing periodic child support payments or maintenance, if applicable;
(6) acts by either spouse resulting in excessive or abnormal expenditures or destruction, concealment, or fraudulent disposition of community property, joint tenancy, or other property held in common;
(7) the contribution by one spouse to the education, training, or increased earning power of the other spouse;
(8) the property brought to the marriage by either spouse;
(9) the contribution of a spouse as homemaker;
(10) Marital misconduct, including adultery and cruel treatment, by either spouse during the marriage; and
(11) Any history or pattern of family violence, as defined by Section 71.004 of the Texas Family Code.
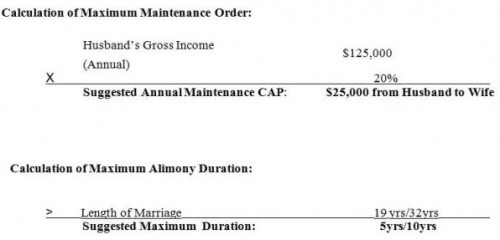
The maximum amount of spousal support that courts may award is the lesser of $5,000.00 per month or 20 percent of the payer’s average gross monthly income. This is the maximum amount of maintenance the court orders.
However, in all circumstances, the law provides that the Court shall order maintenance for the shortest reasonable period that allows the recipient to earn sufficient income to meet his or her “minimum reasonable needs” and as follows:
The Texas law mandates the maximum duration of support as follows:
Maintenance shall be paid for a maximum of:
• 5 years, if due to family violence conviction and marriage is under 10 years;
• 5 years, if marriage is between 10 and 20 years;
• 7 years, if marriage is between 20 and 30 years;
• 10 years, if marriage is 30 years or more;
except in the case of an incapacitating physical or mental disability, in which case the award may last as long as the disability.
In addition, the law allows the Texas Family Law Courts to terminate maintenance if the recipient “cohabits with another person in a permanent place of abode on a continuing, conjugal basis.”
Sample Calculation of Texas Spousal Support Maintenance:
Ho! Ho! Ho! Texas Children’s Visitation Schedules and the Holidays
The Holiday season is now upon us and hopefully all parents have worked out the upcoming visitation schedules for the 2011 Holiday Season. But if not….. Here is a reminder of the current Texas Family Law Code’s Standard Possession Order for Holidays.
§ 153.314. Holiday Possession Unaffected by Distance Parents Reside Apart.
The following provisions govern possession of the child for certain specific holidays and supersede conflicting weekend or Thursday periods of possession without regard to the distance the parents reside apart. The possessory conservator and the managing conservator shall have rights of possession of the child as follows:
Christmas Break:
(1) the possessory conservator shall have possession of the child in even-numbered years beginning at 6 p.m. on the day the child is dismissed from school for the Christmas school vacation and ending at noon on December 28, and the managing conservator shall have possession for the same period in odd-numbered years;
(2) the possessory conservator shall have possession of the child in odd-numbered years beginning at noon on December 28 and ending at 6 p.m. on the day before school resumes after that vacation, and the managing conservator shall have possession for the same period in even-numbered years;
Thanksgiving:
(3) the possessory conservator shall have possession of the child in odd-numbered years, beginning at 6 p.m. on the day the child is dismissed from school before Thanksgiving and ending at 6 p.m. on the following Sunday, and the managing conservator shall have possession for the same period in even-numbered years;
Child’s Birthday:
(4) the parent not otherwise entitled under this standard order to present possession of a child on the child’s birthday shall have possession of the child beginning at 6 p.m. and ending at 8 p.m. on that day, provided that the parent picks up the child from the residence of the conservator entitled to possession and returns the child to that same place;
Father’s Day:
(5) if a conservator, the father shall have possession of the child beginning at 6 p.m. on the Friday preceding Father’s Day and ending on Father’s Day at 6 p.m., provided that, if he is not otherwise entitled under this standard order to present possession of the child, he picks up the child from the residence of the conservator entitled to possession and returns the child to that same place;
Mother’s Day:
(6) if a conservator, the mother shall have possession of the child beginning at 6 p.m. on the Friday preceding Mother’s Day and ending on Mother’s Day at 6 p.m., provided that, if she is not otherwise entitled under this standard order to present possession of the child, she picks up the child from the residence of the conservator entitled to possession and returns the child to that same place.
Texas child visitation orders may differ from the norm to accommodate family situations so you should always check your decree first! If in doubt about your holiday visitation time’s contact someone who can help you to make sure nothing happens to affect this special season with your children. ‘Tis the Season!
Cohabitation and Domestic Partnership Agreements
Premarital and post-marital agreements in Texas have a complex history immersed in the community property presumption, the sate constitution, statutes and case law. Originally, such agreements were found to be unenforceable. But with amendments to the Texas Constitution, evolving statutes, recent case law, and improved draftsmanship, such agreements are now enforceable under contract law.
For some couples living together is a precursor to marriage; for others, there is no intent to ever marry, or the law prohibits the marriage, as in Texas with same sex marriages. The simple fact is, domestic partnership agreements involve a wide variety of circumstances, which may or may not involve the gay or lesbian couple.
Many couples choose to live together so they do not lose certain benefits under current rules of social security, military and insurance disability programs, or to stop those benefits from being taken away from their children. In other cases, couples who are divorced, and who may have children, may want to protect certain assets. In situations such as trust funds or inherited funds, beneficiaries simply do not want to place family money at risk. Other couples choose to shelter their own resources from the real or perceived obligations of their partner.
The marital agreement is considered to be a contract under Texas law. The premarital agreement must be in writing and signed by both parties. No actual consideration is required; however, to conform with contractual law, it may be wise to provide benefits for the non-monied party to avoid a later finding of unconscionability, particularly if the financial condition of the non-monied party under the agreement will be poor.
Matters that may be dealt with in a premarital agreement include, but are not limited to, the following:
- the right to buy, sell, use, transfer, exchange, abandon, lease, consume, expend, assign, create a security interest in, mortgage, encumber, dispose of, or otherwise manage and control property;
- the rights and obligations of each of the parties in any of the property of either or both of them whenever or wherever acquired or located;
- the disposition of property on separation, marital dissolution, death, or the occurrence or nonoccurrence of any other event;
- the modification or elimination of spousal support;
- the making of a will, trust, or other arrangement to carry out the provisions of the agreement;
- the ownership rights in and disposition of the death benefit from a life insurance policy;
- the choice of law governing the construction of the agreement; and
- any other matter, including their personal rights and obligations, not in violation of public policy or a statute imposing a criminal penalty.
Child support may not be adversely affected by a premarital agreement. Therefore, provisions providing for the elimination of child support upon separation or divorce are unenforceable. However, provisions for private education, college expenses, and choice of residence may be included, but may still be reviewed by a court to determine if they are in keeping with public policy.
In post-marital agreements, it has been noted that a fiduciary duty exists that is not present in pre-marital agreements between spouses or prospective spouses. Case law states that a confidential relationship between husband and wife imposes the same duties of good faith and fair dealing on spouses as required of partners and other fiduciaries. However, adverse parties who have retained independent counsel may not owe fiduciary duties to one another. Texas Legislature enacted Section 4.105 with the understanding that married spouses owing fiduciary duties to one another would negotiate and execute post-marital agreements. Not withstanding these duties, the legislature manifested the strong policy preference that voluntarily made post-marital agreements are enforceable.
Cohabitation, domestic partnership, premarital and post-marital agreements may be as creative as a party determines necessary. However, care must be given to see that such agreements protect the party, keep with public policy, and adhere to current Texas family law and applicable contractual law.


