Texas Child Support Guidelines Update
PLEASE READ UPDATE (2019)
Texas Child Support Guidelines Change-
Effective Sept. 1, 2019
Effective September 1, 2019 The Texas Child Support Division of the Attorney General increased the Maximum child Support under the Texas Child Support Guidelines from $8,550 to the “new cap”of net monthly resources to $9200 annually. This change in the law will increase the amount of maximum child support from of $1,710.00 to $1,840.00 monthly (20% of $9200. For one child)
CLICK TO READ MORE ON THIS UPDATE
PRIOR GUIDELINES
On September 1, 2013: Important Texas Child Support Guideline Changed!
The Texas Child Support Division of the Attorney General increased the “CAP” on net resources for purposed Child Support from the past amount of $7500 to be $8550, which became effective Sept. 1, 2013.
This “Cap Increase” affects any child support case filed or pending after September 1, 2013.
Under the Texas Family Code §154.125 the guidelines for Child Support are as follows:
(a) The guidelines for the support of a child in this section are specifically designed to apply to situations in which the obligor’s monthly net resources are not greater than $8,500 or the adjusted amount determined under Subsection (a-1), whichever is greater.
(a-1) The dollar amount prescribed by Subsection (a) above is adjusted every six years as necessary to reflect inflation. The Title IV-D agency shall compute the adjusted amount, to take effect beginning September 1 of the year of the adjustment, based on the percentage change in the consumer price index during the 72-month period preceding March 1 of the year of the adjustment, as rounded to the nearest $50 increment. The Title IV-D agency shall publish the adjusted amount in the Texas Register before September 1 of the year in which the adjustment takes effect. For purposes of this subsection, “consumer price index” has the meaning assigned by Section 341.201, Finance Code.
(a-2) The initial adjustment required by Subsection (a-1) shall take effect September 1, 2013. This subsection expires September 1, 2014.
(b) if the obligor’s monthly net resources are not greater than the amount provided by Subsection (a), the court shall presumptively apply the following schedule in rendering the child support order:
CHILD SUPPORT GUIDELINES
BASED ON THE MONTHLY NET RESOURCES OF THE OBLIGOR
- 1 child 20% of Obligor’s Net Resources
- 2 children 25% of Obligor’s Net Resources
- 3 children 30% of Obligor’s Net Resources
- 4 children 35% of Obligor’s Net Resources
- 5 children 40% of Obligor’s Net Resources
- 6+ children Not less than the amount for 5 children
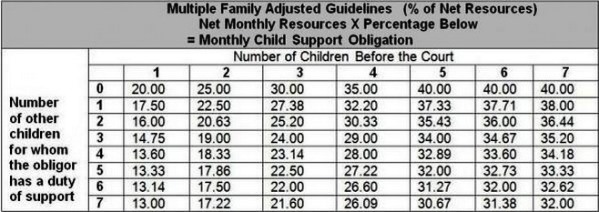
Depending on the number of other children an obligor has a duty to support, the percentage of child support may be lower. For example, if the obligor was previously married and has 1 child to support in the previous marriage, the amount of support paid for one child before the court decreases to 17.50 percent. See the chart below.
Net resources are determined by deducting the following from the obligor’s income:
1. Social Security Taxes;
2. Federal Income Tax based on the tax rate for a single person claiming one personal exemption and the standard deductions;
3. State Income Tax;
4. Union Dues (if such deductions are being withheld); and
5. Expenses for Health Insurance Coverage for Obligor’s Child(ren) (if such deductions are being withheld).
New Texas Laws Affecting Families – In Effect Beginning Sept. 1, 2013
Texas House Bill 845: Standard Possession Order
Amends Family Code provisions relating to standard Texas court orders for possession of a child in suits affecting the parent-child relationship. The bill specifies that written notice for purposes of such possession may now be provided by e-mail or facsimile. The bill provides additional alternative beginning and ending possession times under the standard possession schedule for Mother’s Day weekend and for Thursdays and weekends during the regular school term. The bill also repeals provisions relating to a petition by a conservator for additional periods of possession of or access to a child after the conclusion of the conservator’s military deployment.
Texas House Bill 847: Spousal Maintenance
Amends the Family Code to specify that the agreement for payment of maintenance that is enforceable by contempt is an agreement for periodic payments of Texas spousal maintenance and to prohibit the enforcement by contempt of any provision of an agreed order for maintenance exceeding the amount of periodic support a court could have ordered. The bill authorizes a court to order income withholding in a proceeding in which there is a court-approved agreement for periodic payments of spousal maintenance voluntarily entered into between the parties but prohibits such an order to the extent that any provision of the order exceeds the amount of periodic support the court could have ordered or for any period of maintenance beyond the period the court could have ordered. The bill also specifies that a division of property and any contractual provisions under the terms of a court-approved agreement incident to divorce or annulment are enforceable in the same manner as a division of property provided for in a decree of divorce or annulment. The bill updates relevant enforcement provisions to reflect this inclusion.
Texas House Bill 3017: VA Disability Benefits and Net Resources
Amends Family Code provisions relating to the calculation of net resources for the purpose of determining child support liability. The bill includes U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs disability benefits, other than non-service-connected disability pension benefits, among the types of income considered resources. The bill authorizes a court, in determining whether an obligor is intentionally unemployed or underemployed, to consider evidence that the obligor is a veteran who is seeking or has been awarded either veteran disability benefits or non-service-connected disability pension benefits. The bill also updates language regarding the wage and salary presumption used in the absence of evidence of a party’s resources.
Texas House Bill 847: Enforcement of a Child Support Order by Contempt
Amends Family Code provisions relating to motions to enforce a final order in a suit affecting the parent-child relationship. The bill establishes that a court, in hearing such a motion, is not precluded from awarding court costs and reasonable attorney’s fees to the movant upon finding that the respondent is not in contempt with regard to the underlying order. The bill repeals a provision prohibiting the court from finding a respondent in contempt for failure to pay child support under certain conditions and a provision authorizing the court to award the petitioner court costs and reasonable attorney’s fees in a Texas child support enforcement hearing under certain conditions.
Texas Senate Bill 129: Venue for a Protective Order Application:
Amends the Texas Family Code to expand the venue for filing an application for a protective order against family violence to include any county in which the family violence is alleged to have occurred.
Behind on Texas Child Support Payments? Possible Trouble Renewing Your Texas Drivers License!
Texas HB 1846: Suspension or denial of issuance or renewal of a license for failure to pay child support
The court or Title IV-D agency may stay an order suspending a license conditioned on the individual’s compliance with:
- A reasonable repayment schedule that is incorporated in the order
- The requirements of a reissued and delivered subpoena
- The requirements of any court order pertaining to the possession of or access to a child
The court or Title IV-D agency may not stay an order unless the individual makes an immediate partial payment in an amount specified by the court or Title IV-D agency. The amount specified may not be less than $200.
A licensing authority that receives the information shall refuse to accept an application for issuance of a license to the obligor or renewal of an existing license of the obligor until the authority is notified by the child support agency that the obligor has:
- Paid all child support arrearages
- Made an immediate payment of not less than $200 toward child support arrearages owed and established with the agency a satisfactory repayment schedule for the remainder or is in compliance with a court order for payment of the arrearages
- Been granted an exemption as part of a court supervised plan to improve the obligor’s earnings and child support payment
- Successfully contested the denial of issuance or renewal of license
An order suspending a license rendered before the effective date of this Act is governed by the law in effect on the date the order was rendered.
Texas HB 1846 takes effect September 1, 2013
Fathers Divorcing in Texas
As family relationships grow and develop, conflicts can arise. Family law provides guidelines and offers legal alternatives to remedy the issues family members often face.
At The Nacol Law Firm PC, Mark A. Nacol addresses the concerns of clients throughout Texas in a wide scope of family law matters that include:
- Divorce
- Modifications and post-divorce modifications
- Child custody and child support
- Visitation and residence restrictions
- Interstate jurisdiction
- Alimony and spousal support
- Paternity and voluntary legitimating
- Property division
- Adoption
- Prenuptial and marital and domestic relating agreements
- Post-marital agreements
- Enforcement of court orders
- Same-sex unions or same-sex marital conflicts and dissolution options
- Grandparent custody and visitation rights