How Much is Texas Child Support? Texas Child Support Guidelines
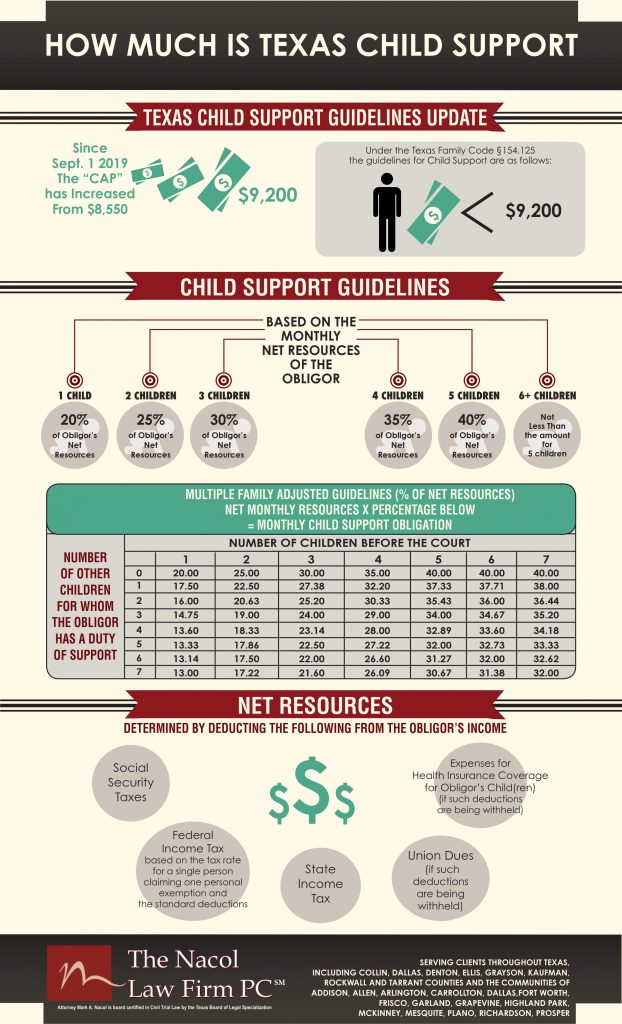
Effective September 1, 2019 The Texas Child Support Division of the Attorney General increased the Maximum child Support under the Texas Child Support Guidelines from $8,550 to the “new cap”of net monthly resources to $9200 annually. This change in the law will increase the amount of maximum child support from of $1,710.00 to $1,840.00 monthly (20% of $9200. For one child)
Texas Family Code §154.125(a)(1) requires that every six years the presumptive amount of net resources to which the child support guidelines apply shall be reviewed and adjusted for inflation by the Texas Office of the Texas Attorney General (OAG). That section sets out the formula for doing so based on the consumer price index. The last adjustment was done in 2013 when the current amount of $8550 per month was established.
How does the “cap” work and what could this mean for you? If your net monthly resources are less than $8,550, the child support obligation will not change on Sept. 1. You are under the “current cap” and lower than the “new cap”. All stays the same.
If you are currently going through litigation and your net monthly resources exceeds $8,550 and the Court orders child support prior to September 1, 2019, Texas Child Support Guidelines will mandate that the Court apply the appropriate child support percentage to the first $8,550 in net monthly resources based on the number of children. But, if the Court orders child support after September 1, 2019, it will apply the new appropriate child support percentage to the first $9,200 in net monthly resources.
Child support under the guidelines is determined by applying the applicable percentage, beginning at 20% for one child and increasing incrementally for each additional child, to the net resources amount. If a child support obligor has monthly net resources over $9200, a party seeking above the guideline’s child support has the burden of proving to the court that additional support should be ordered according to factors set out in Texas Family Code §154.126.
Important to Know: The new “cap” increase of September 1, 2019 will not automatically increase the obligor’s existing child support obligation. Any change in child support standing before September 1, 2019, can only occur through the court with a modification order to increase the child support to the new “Cap” amount of $9200. After September 1, 2019, any new suit for child support will be subject to the new “cap”.
Please review the Texas Office of the Texas Attorney General (OAG) website for a child support calculator for the new breakdown: https://csapps.oag.texas.gov/monthly-child-support-calculator
The Nacol Law Firm PC
8144 Walnut Hill Lane
Suite #1190
Dallas, Texas 75231
Nacollawfirm.com
Child Support: Gender Neutral Pro Rata Child Support Obligations
One of the most frequent inquiries we receive at The Nacol Law Firm is whether child support obligations are equally applied between Mothers and Fathers. When a parent is considering a divorce or a union break up with the child’s other parent, who pays for child support and medical/dental insurance for the child, for how long and according to what guidelines?
The State of Texas (Texas Family Code Ch 154) Sec. 154.001. SUPPORT OF CHILD. (a) The court may order “Either” or “Both” parents to support a child in the manner specified by the order: (1) until the child is 18 years of age or until graduation from high school, whichever occurs later; (2) until the child is emancipated through marriage, through removal of the disabilities of minority by court order, or by other operation of law; (3) until the death of the child; or (4) if the child is disabled as defined in this chapter, for an indefinite period.
The State of Texas child support laws dictate that children are entitled to financial support from both parents. Texas establishes child support guidelines to determine how much an average child will need. The guidelines provide for a basic amount of support to the parent who receives it based on the other parent’s income and number of children to be supported. However, there may be special circumstances that justify the court’s deviation from the standard amount of child support. Extraordinary expenses can be taken into consideration, including medical expenses or high childcare costs and other specific exceptions.
The State of Texas also supports that a Father and Mother should have the relatively equal rights to the child and should share in the child’s care and support. What does that mean? If Mom or Dad each have standard access and possession 50% of the time, then the Father and Mother should pay guideline support for the care of the child. Yes, Father and Mother.
With a substantial rise of mothers paying child support in the United States, many women are reevaluating their situations, when they find out Dad will not be paying all expenses and child support and be prorated when raising the child 50% of the time. Today’s mothers are the primary breadwinners in four out of 10 U.S. families (Pew Research).
Texas statutes dictate specific Child Support guidelines and, like it or not, other than rare exceptions, neither parent can escape this obligation! Many mothers will plea that they cannot work because of their obligation to the care of the child or will under-employ to try to escape paying their rightful share of the child’s support. But in today’s world many parents either share 50/50 time with their child or father may be the primary custodial parent.
If the mother refuses to pay court-ordered child support, there may be several enforcement options. A contempt of court action can hold the mother civilly or criminally liable for not obeying the court’s mandate. If found guilty, the mother may be required to post a bond equal to the amount of child support in arrearages or may have to serve time in jail for contempt. Other actions include suspending the mother’s driver’s license or professional license, intercepting tax refunds or federal payments, denying passports, placing liens on property and reporting the debt to credit bureaus.
CHILD SUPPORT GUIDELINES BASED ON THE MONTHLY NET RESOURCES OF THE OBLIGOR:
- 1 child 20% of Obligor’s Net Resources
- 2 children 25% of Obligor’s Net Resources
- 3 children 30% of Obligor’s Net Resources
- 4 children 35% of Obligor’s Net Resources
- 5 children 40% of Obligor’s Net
- 6+ children Not less than the amount for 5 children
(3/5/2019 FAMILY CODE CHAPTER 154. CHILD SUPPORT https://statutes.capitol.texas.gov/Docs/FA/htm/FA.154.htm 20/47)
For more information on Texas Child Support Guidelines, please go to the Texas Attorney General Child Support Website at: https://csapps.oag.texas.gov/monthly-child-support-calculator
Mark Nacol
Nacol Law Firm
Dallas TX
How Can The Uniform Interstate Family Support Act (UIFSA) Affect Your Family Interstate Jurisdiction Problems?
Are you a parent having trouble collecting your child support for the children because your EX-spouse lives in another state? This has been a problem for many families for a long time. The United States Congress recognized this problem and mandated all states to adopt the Uniform Interstate Family Support Act (UIFSA) to facilitate collection of child support across state lines.
It is no surprise that people move, but when trying to collect child support from an out-of-state parent you may need legal help to avoid unpleasant surprises.
When more than one state is involved in establishing, enforcing or modifying a child or spousal support order, the UIFSA determines the jurisdiction and power of the courts in the different states. The Act also establishes which state’s law will be applied, an important factor as support laws vary greatly among the states.
If there is no current child support order and the child and one parent live in Texas, the order or paternity determination may be established without another state’s involvement. If the parents have sufficient contact with Texas, the court may be able to enter an order even if one parent does not currently live in the state. UIFSA enables Texas and another state to cooperate to establish a child support order if another state’s assistance is needed because of residency issues.
UIFSA permits only one active support order for a case at a time. When there are multiple orders, UIFSA determines which support order will be followed, known as the “controlling order.” Orders may be registered in a different state for enforcement and modification purposes. The initiating state sends the order and documents to the responding state. The responding state registers the order and sends a notice to the other parent. The other parent has 20 days to file written objections regarding the order. If objections are made prior to the deadline, the court will hold a hearing and decide whether the order should be registered.
UIFSA also allows parents to enforce their support orders without the assistance of the state where the obligor (paying parent) lives. A withholding order, in many cases, can be sent directly to the out-of-state obligor’s employer requiring child support be deducted from the parent’s wages. The responding state also has the authority to pursue collection through enforcement hearings, license suspension, or incarceration of the delinquent, non-custodial parent.
If financial or other circumstances have changed, you may also request the court to modify a child support order. UIFSA sets the rules for modification. If either of the parents or the child still lives in the state that issued the controlling order, changes in the support amount must occur there. Otherwise the order may be registered and modified in the child’s home state. The child’s home state is generally where the child has resided for six (6) months with a parent.
If all parties have left the state that issued the controlling order, that state cannot change the support amount. To modify support, the order must be registered for modification in the state of residence of the parent not seeking modification.
UIFSA allows both parents to agree in writing that the state where one parent resides may modify the order and take control of the case. When a state modifies another state’s order, the new support amount is the amount to be collected by all any state in which the obligor resides.
Parents often turn to the Texas Attorney General for assistance in the collection and enforcement of child support, and that can be a good choice. However, parents – especially those who are experiencing continued delays and roadblocks – can hire a private attorney to advocate on their behalf and for the benefit of their children. An attorney can also provide guidance in enforcing and modifying terms of visitation.




